Disclaimer
We assume no responsibility or liability for any loss or damage incurred as a result of any use of the information contained within or downloaded from this website.
If you have any problems, please let us know
How to use the webapp
Firstly, select a species:
Then type a gene into the box, and select the gene you're interested in:
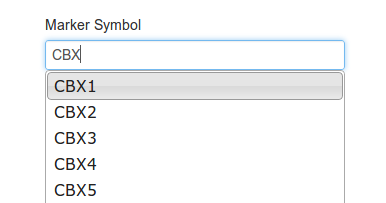
A list of exons from the canonical transcript will appear as below. Select an exon from the list:
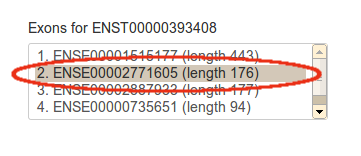
Note that only exons on canonical transcripts are available for now. This will be amended in a future update
There are two options for viewing the data (see below screenshot), a grid view with a single entry in the table per pair, or a genome browser similar to ensembl. If you would like to see individual CRISPRs and not just those belonging to pairs, you must choose the genome browser view.
Table view
If you have chosen the table view, wait for it to load:
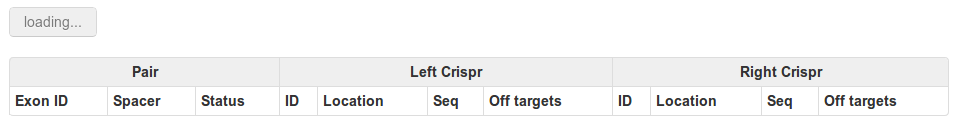
And you will be provided with a view like this:
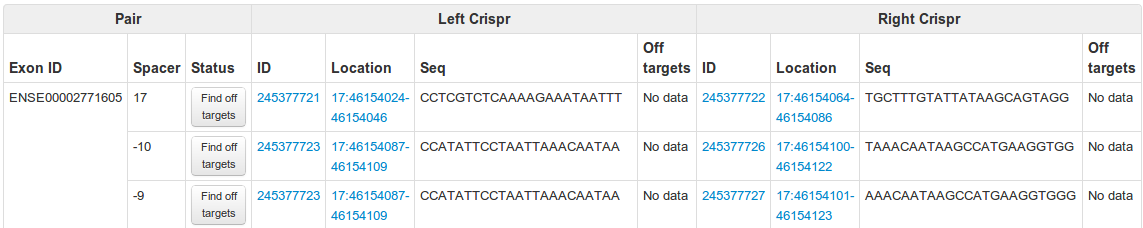
Here you can see all the data for a CRISPR pair, with full details of the CRISPRs it contains. There is also a button labelled 'Find off targets' which when pressed will run a background job that will compute all the off targets for that pair. It should take about 5 minutes but during periods of high usage it could take a lot longer.
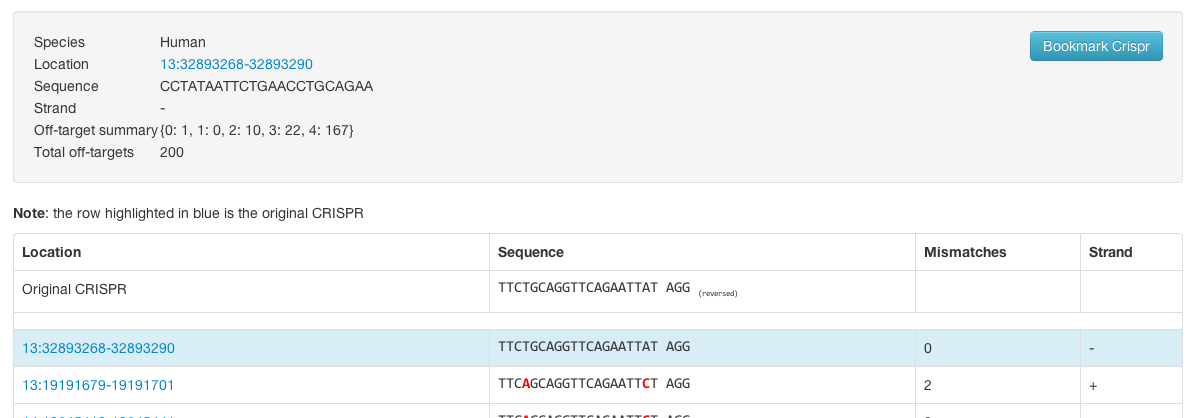
The link in the ID column will take you to a page where you can view individual CRISPR off targets if we have them:
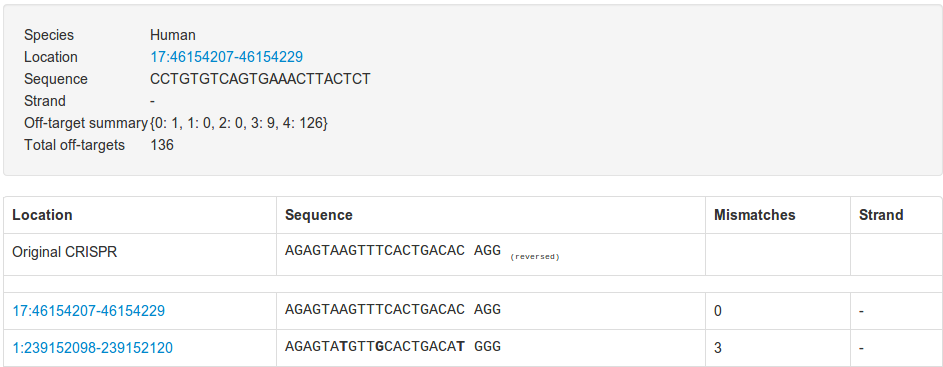
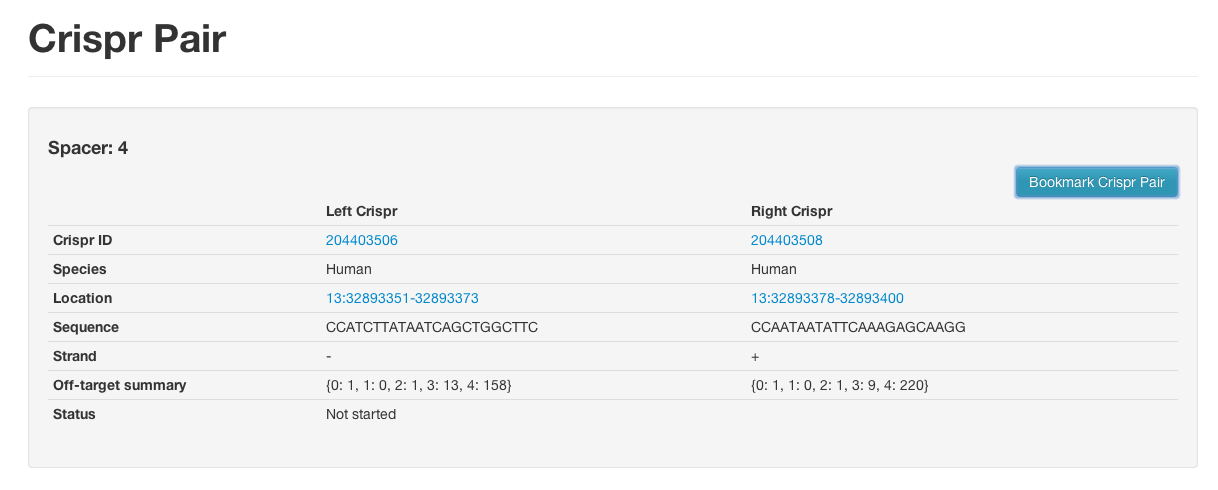
And the pair ID column link will take you to a similar page that will show you all paired off targets:
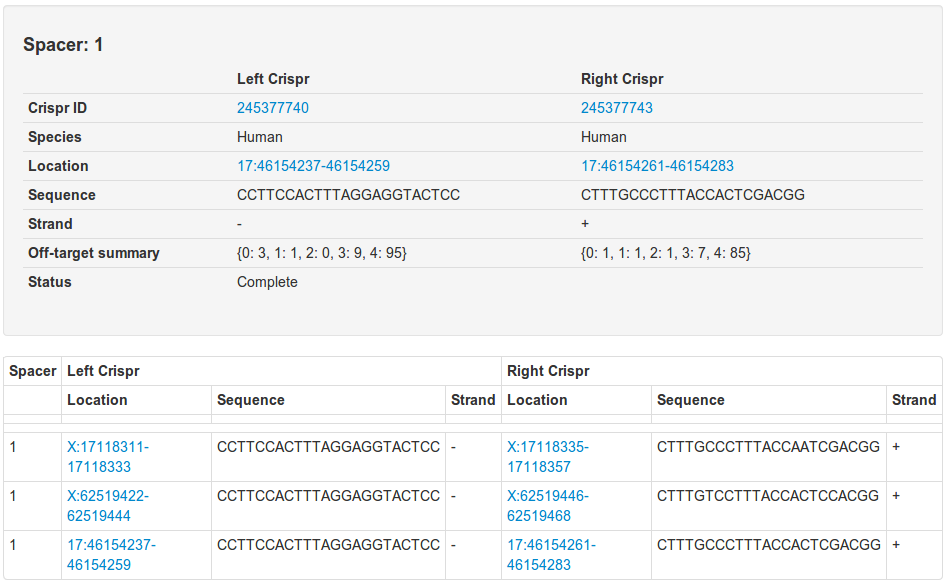
Genome browser view
The genome browser view looks like this:
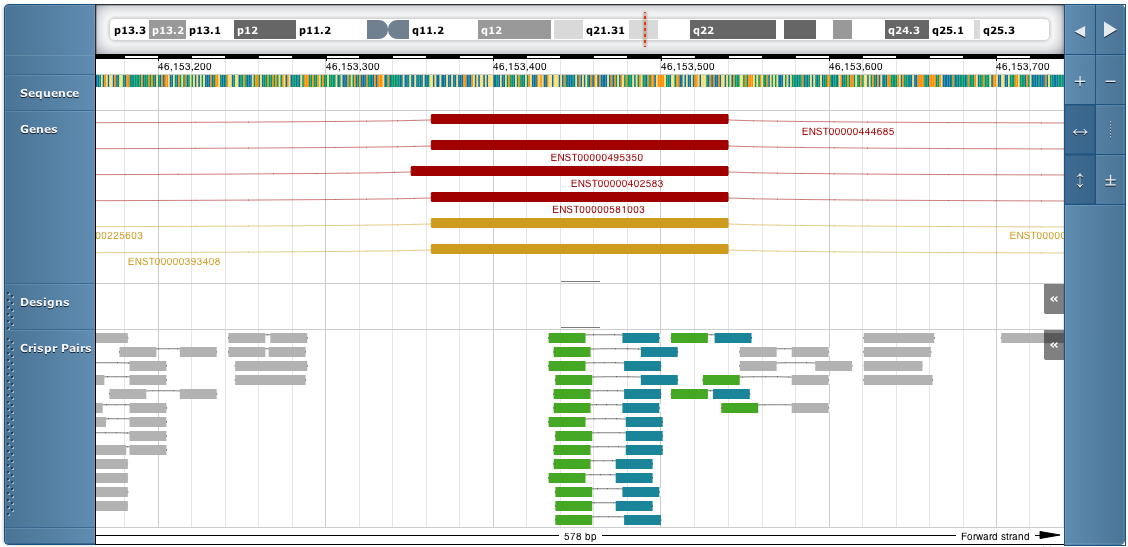
Use the controls on the top right of the genome browser to move left and right or zoom in. You can also move left and right by dragging or scrolling with the mouse.
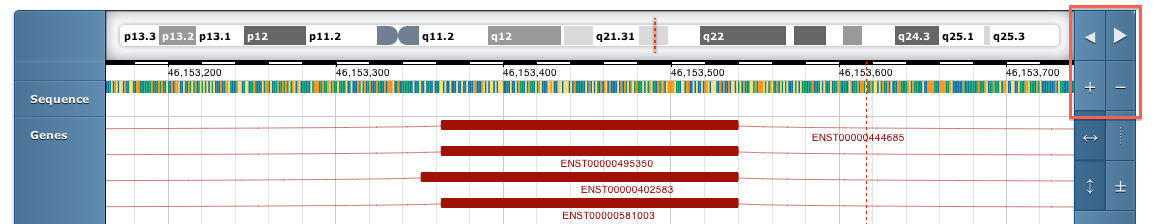
To select a region hold the shift key and drag over the region with the mouse. This will give you the option to submit all crispr and pairs in the region for off-target computation
We have computed off-target data for all crisprs shown in colour. Off-targets have not yet been computed for crisprs shown in grey.
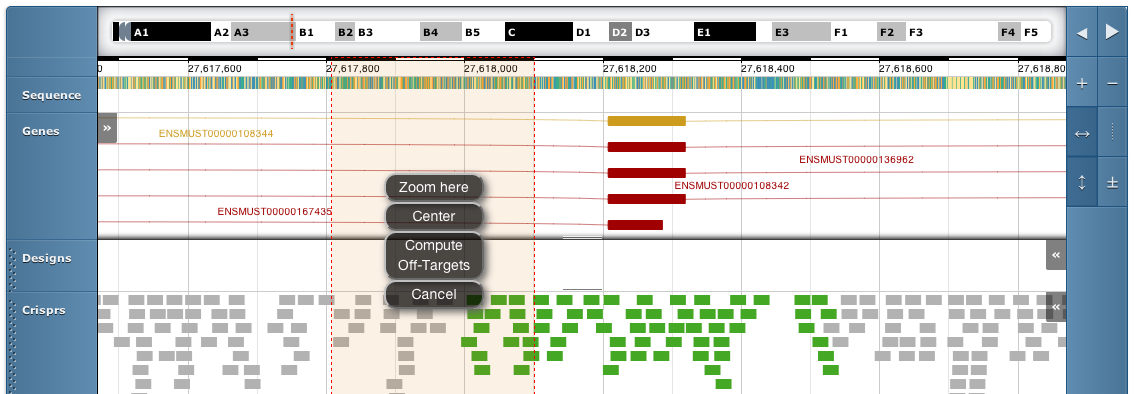
Clicking on a pair will give you more details on that pair, including off-target counts if available:
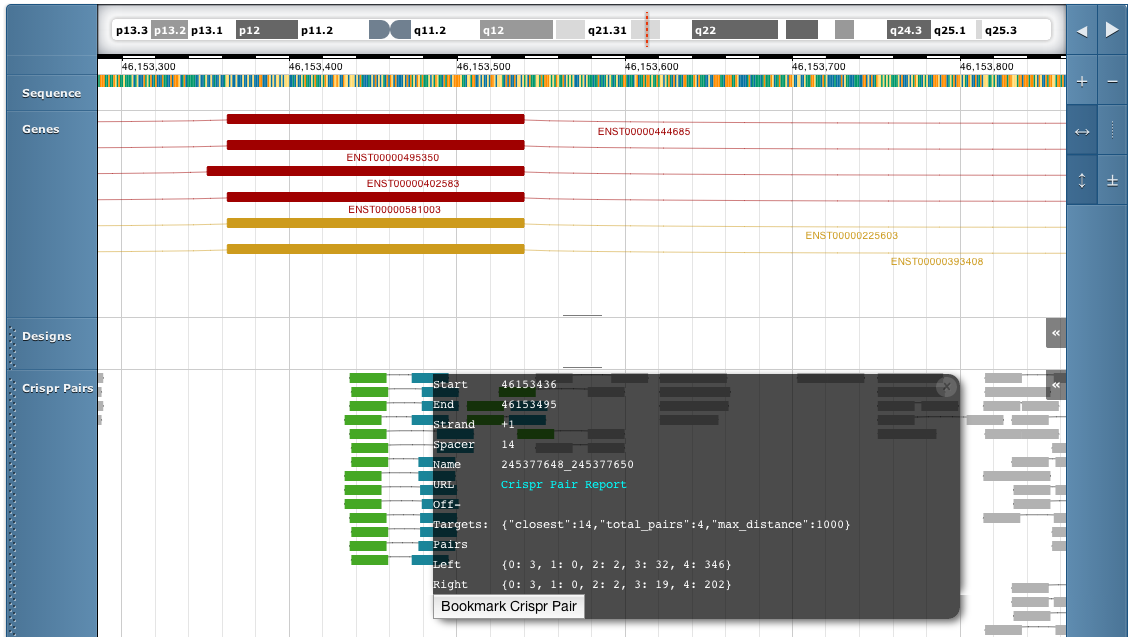 This menu includes a link to the crispr pair report page, which will you give you all the data for that pair.
This menu includes a link to the crispr pair report page, which will you give you all the data for that pair.
Use the controls at the bottom of the screen to display single crisprs:
 This will cause a second track to show up on the browser, which can also be clicked to show off-target counts and report links for individual CRISPRs:
This will cause a second track to show up on the browser, which can also be clicked to show off-target counts and report links for individual CRISPRs:

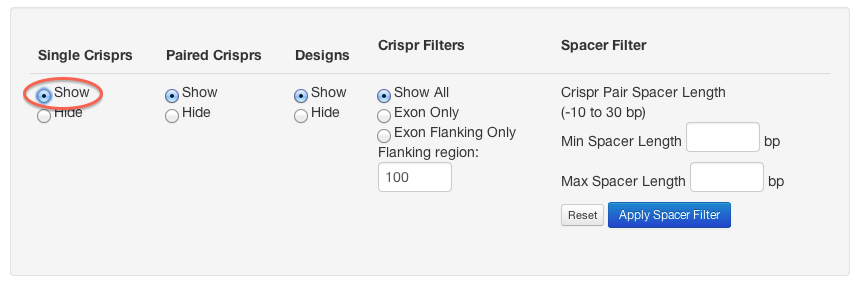
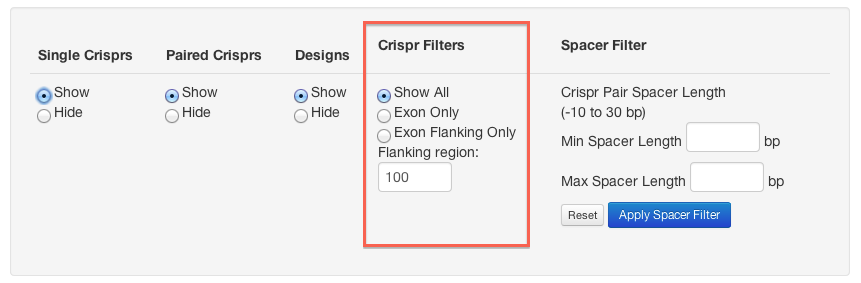
You can choose from the following "Crispr Filters" options:
- Show All: all crisprs and pairs
- Exon Only: crisprs and pairs that are within an exon
- Exon Flanking Only: crisprs and pairs that lie either side of an exon (specify the maximum distance from the exon in "Flanking region" - default is 100 bp)
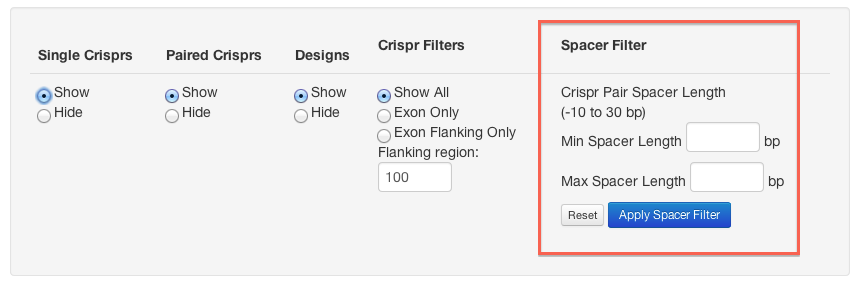
When crispr pairs are displayed you can filter them so that only those with a spacer in the specified range are shown.
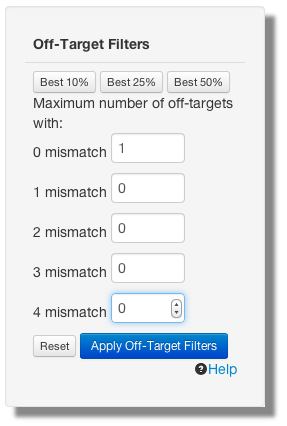
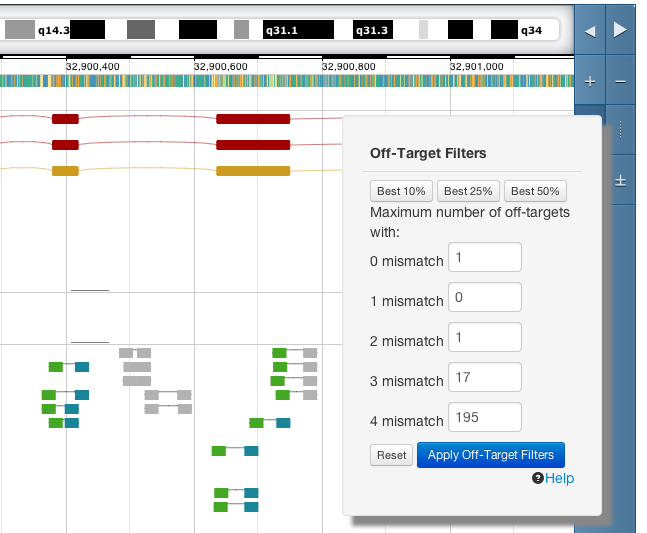
Crisprs and crispr pairs can be filtered based on the number of off-targets they have. Enter the maximum
number of off-targets to allow in each of the mismatch categories. Crisprs that we have not computed off-targets for (those shown in grey) will not be removed by this filter.
For example, to see only crisprs which have no off-targets with up to 4 mismatches enter the following then apply the filter.
 There will always be 1 or more off-targets in the 0 mismatch (perfect match) category because the off-target computation identifies the original crispr site.
There will always be 1 or more off-targets in the 0 mismatch (perfect match) category because the off-target computation identifies the original crispr site.
For a more relaxed search increase the number of off-targets allowed and apply the filter again. Alternatively, use the "Best.." buttons to see crisprs with off-target counts in the 10th, 25th or 50th percentile of our data.
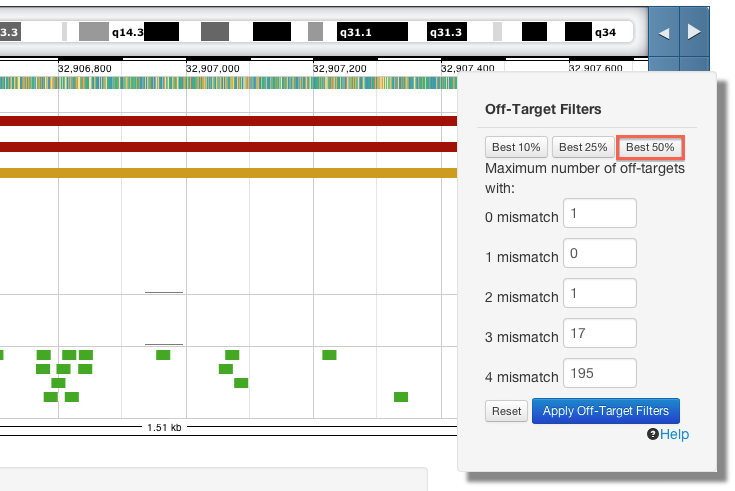 You can drag the filter menu anywhere on the page to make it easier to see the effect of the filtering in your region of interest.
You can drag the filter menu anywhere on the page to make it easier to see the effect of the filtering in your region of interest.
When this filter is applied to the paired crisprs the off-targets of the left and right crispr are counted independently. If either one of the individual crisprs in the pair does not meet the filter requirements then the pair is hidden.
 Click on a pair and go to the "Crispr Pair Report" page to see details of paired off-targets.
Click on a pair and go to the "Crispr Pair Report" page to see details of paired off-targets.
Bookmarks
Login to WGE using your Google account in order to bookmark crisprs and crispr pairs
Add or remove bookmarks on the report pages for a crispr or crispr pair
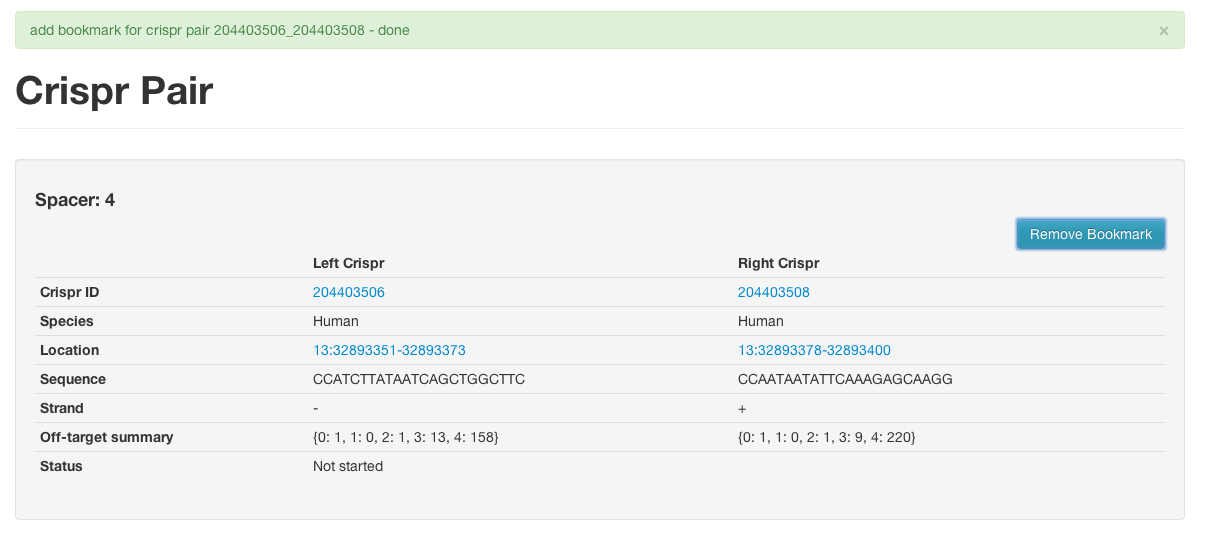
View summary information about all your bookmarked items
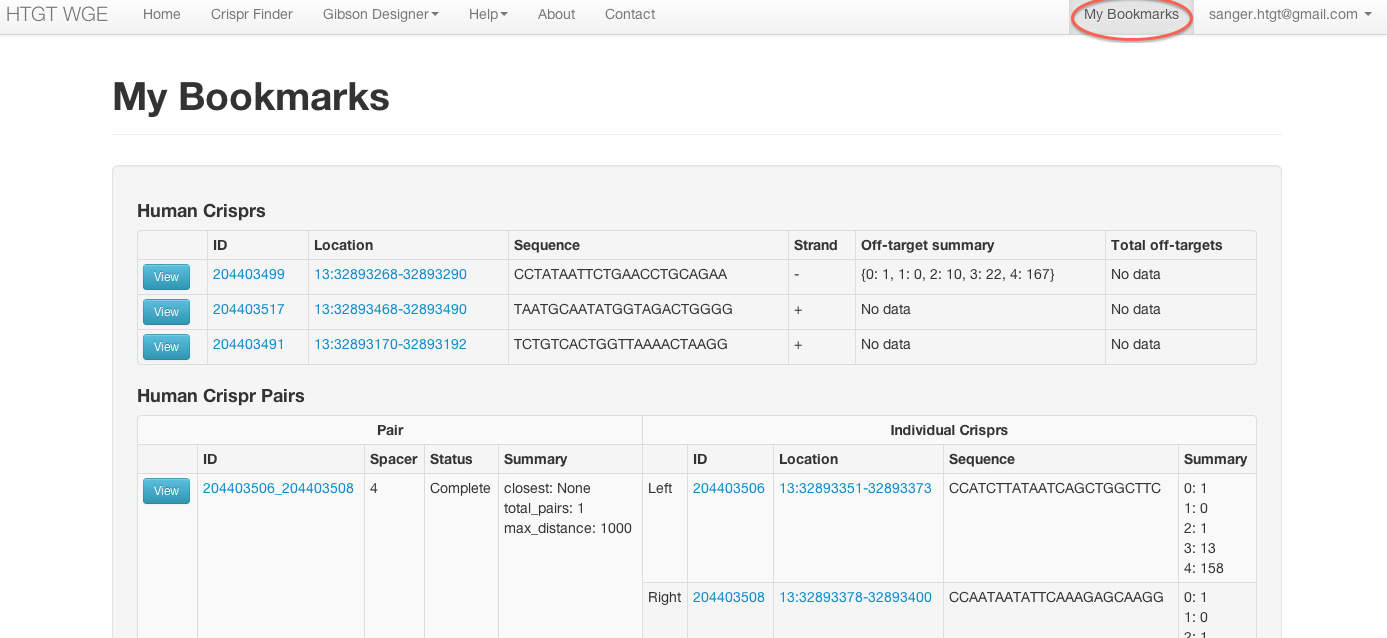
When logged in your bookmarked crisprs and pairs will appear on additional tracks in the genoverse view
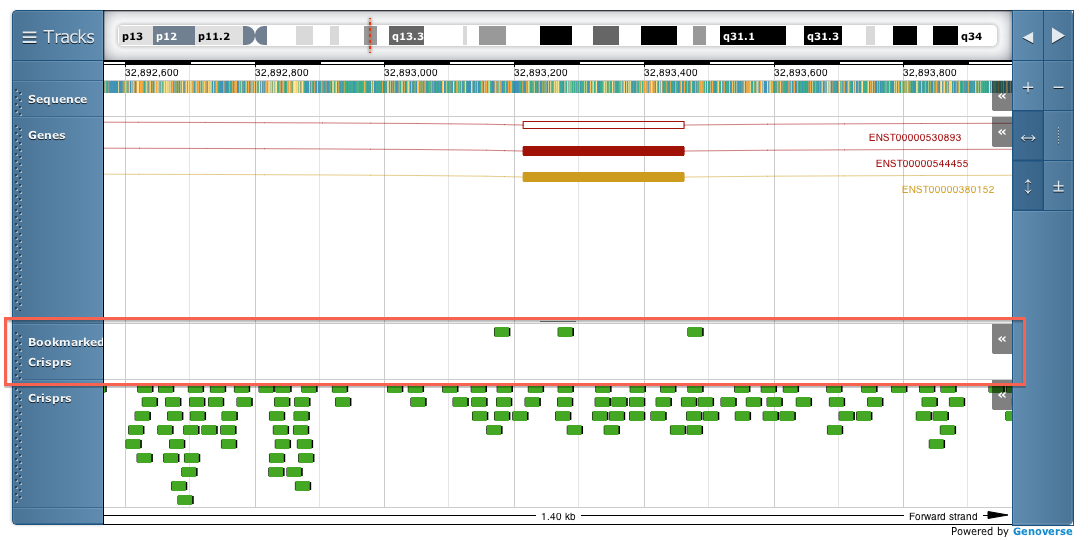
Off targets
An off target is a site in the genome that may be cut by a given CRISPR, where the site is not the original CRISPR site we intended to cutref.
The site must contain a PAM site (NGG), and the sequence will be similar to the given CRISPR sgRNA.
Cutting has been seen with up to 5 mismatches depending on their proximity to the PAM; mismatches closer to the PAM site are less tolerated than those further away.
Cutting has also been seen at a reduced efficiency at NAG PAM sites, but we do not currently look at those when evaluating off targets; this option will be coming in a later version.
Explanation of off target summaries
Individual
The individual off target summaries are formatted like this:
0: 1
1: 0
2: 3
3: 26
4: 89
The left column is the number of mismatches (this is the grouping)The right column is the number of off-targets we found with that many mismatches
Note: We include the original CRISPR site in the off target summary, so you will always see 1 off target in the 0 mismatches column
So in the above example, this CRISPR has:
0 off targets with 0 mismatches (other than itself)
0 off targets with 1 mismatch
3 off targets with 2 mismatches
26 off targets with 3 mismatches
89 off targets with 4 mismatches
For a total of 118 off targetsOur selection criteria for a 'good' CRISPR is:
0: 1
1: 0
2: 0
Paired
The paired off target summaries are formatted like this:
closest: 23
total_pairs: 3
max_distance: 1000
closest tells you how close the nearest valid paired off target we found is. A value of 23 means we found a paired off target with a spacer of 23 bases, which is very close (the pair should be avoided if there's a better option.) If you see 'None' in this column it means we did not find a valid pair within the set distance. Note: this value will never be the original pair.
total_pairs tells you how many paired off targets we found.
Note: we include the original pair in this total, so the minimum value you will see here is 1.
max_distance tells you what the maximum allowed spacer was for us to count a paired off target as valid.
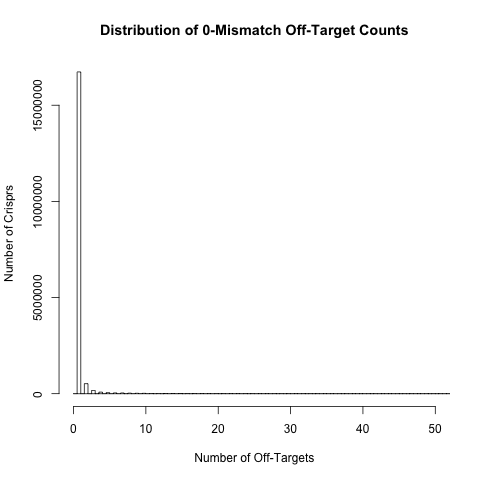
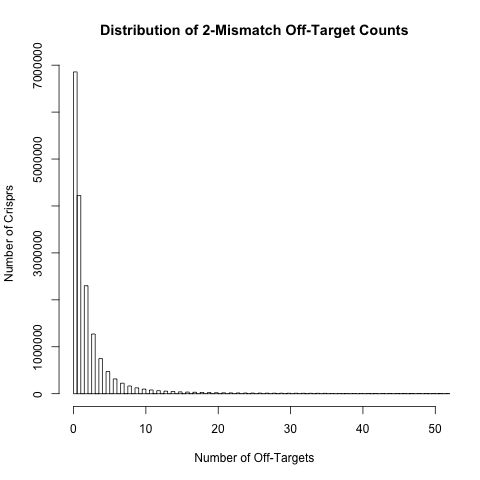
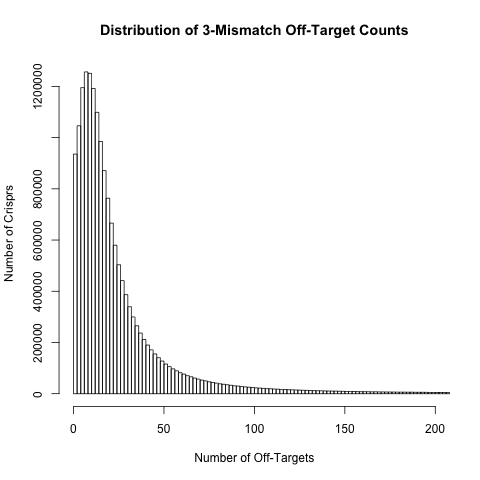
Off-target count distributions
For each crispr we have calculated the number of off-target sites with 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 mismatches. The histograms below show the distribution of these off-target counts. These distributions are based on approximately 18 million crispr sites in exons and their surrounding regions (200bp either side of the exon) in the human genome.
Calculating CRISPR off targets
To calculate off targets for CRISPRs we use the CRISPR-Analyser package. For details about how this works please see our developer help page.
Calculating off targets for CRISPR pairs
Paired CRISPRs can be used with a modified Cas9 protein to reduce off targetsref. What we call a 'Paired CRISPR' is simply two CRISPRs in close proximity (within 50bp~), that are located on opposite strands.
A nickase version of the Cas9 protein is used together with the two CRISPRs, meaning that we still get a break at the the desired site due to the two nicks being in close proximity, and (hopefully) all off targets are repaired without indels as there is only a single stranded break.
This does not completely stop off target cutting; if off targets of either CRISPR in the pair happen to be within close proximity, you could potentially see an unwanted double stranded break. We call this a 'paired off target'.
We calculate any potential paired off targets in our application by checking if any two individual off targets are within 1kb of each other, and if so we store it in our database.
Explanation of CRISPR pair status column
When viewing CRISPR pairs you will notice that they usually have a status, for example:
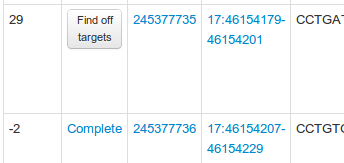 If you see a 'Find off targets' button then this pair has not yet been created, and if it does have a status you can see an explanation in the table below:
If you see a 'Find off targets' button then this pair has not yet been created, and if it does have a status you can see an explanation in the table below:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Bad crispr in pair | One (or both) of the CRISPRs involved in the pair is 'bad'; we define bad as a CRISPR with more than 2000 potential off targets. For bad CRISPRs we don't store their individual off targets, only the summary string. |
| Error | Something has gone wrong while attempting to find CRISPR off targets |
| Not started | No one has requested off target data for this CRISPR pair yet |
| Pending | The off target finding job is in the queue waiting to begin |
| Finding Individual off targets | The job has been started |
| Persisting individual off targets | Individual off targets have been found, and are now being inserted into the database |
| Calculating paired off targets | Individual off targets are in the database, so paired off targets are now being computed |
| Complete | Off target data for the individual crisprs is in the database, as well as paired data |
This tool is being continuously developed and extended. If you wish to contact us about it, please do so at wge@sanger.ac.uk
References
Hsu P.D. et al (2013) DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nature Biotechnology 31, 827â832 doi:10.1038/nbt.2647
Quinlan A.R. and Hall I.M., (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 26, 6, pp. 841â842
Ran. F.A. et al. (2013) Double Nicking by RNA-Guided CRISPR Cas9 for Enhanced Genome Editing Specificity. Cell 154, 1380â1389
Shen, B. et al. (2014) Efficient genome modification by CRISPR-Cas9 nickase with minimal off-target effects. Nature Methods doi:10.1038/nmeth.2857